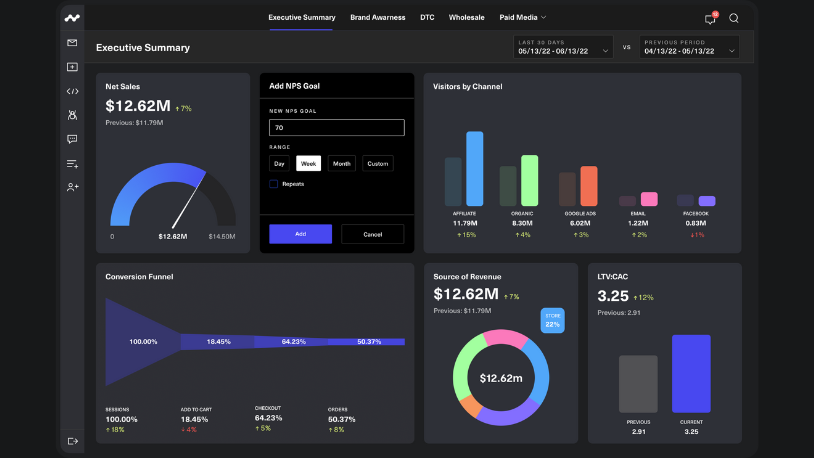
Metrics that matter: LTV to CAC
If we had to pick one metric and one metric only for evaluating e-commerce success, it’d be the LTV to CAC ratio. Retaining customers for a longer period of time and keeping customer acquisition costs low is fundamental for a sustainable and profitable business. Let’s dive into the significance of this metric, discuss how to calculate it, and show how CorralData can make the process simple for your e-commerce business.
What is the LTV to CAC ratio?
LTV stands for Lifetime Value, which measures the average revenue generated by a customer over their entire relationship with the business. The metric includes both the initial sale and subsequent purchases made by the customer. One-off sales are valuable, but the real power lies in creating a high LTV and encouraging customers to become repeat buyers.
CAC stands for Customer Acquisition Cost, representing the cost incurred to acquire a new customer. It includes paid media expenses allocated to customer acquisition efforts and the costs incurred through sales and marketing activities. Ultimately, a lower CAC can help companies to maximize their revenue and profitability.
The LTV to CAC ratio provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of a company’s marketing efforts and its overall profitability. Ideally, the LTV to CAC ratio should be 3:1 or higher—that means making at least three times more than what you spend on acquiring a customer. If your LTV to CAC is less than this, it’s time to take action and adjust your strategy!
How to calculate your LTV to CAC ratio
To calculate the LTV to CAC ratio, you first need to calculate your company’s LTV and CAC separately.
To calculate LTV, an e-commerce brand needs to identify and link orders to specific customers. This requires capturing detailed customer data and linking it to a unique identifier, such as an email address. Tracking purchase history, item details, and customer preferences allows for more accurate LTV calculations. Tools like Shopify, Magneto, BigCommerce, and WooCommerce can streamline the process of collecting this data.
To calculate CAC, divide your total paid media spend and other marketing expenses by the number of newly acquired customers during the same period. While this formula provides a general estimate, it is ideal to differentiate between spend targeting existing customers versus new customers for a more accurate calculation.
After calculating the LTV and CAC figures, the next step is to determine the ratio by dividing the LTV by the CAC. Again, successful businesses are looking for a 3:1 ratio or higher for this metric.
Using CorralData to calculate LTV to CAC
Calculating LTV to CAC isn’t always an easy task, unfortunately. The data required for the calculation is typically spread across a few systems, including your e-commerce platform, Google Analytics, Meta Ads and Google Ads, to name a few.
The good news? CorralData streamlines organizing and linking up customer data from these platforms and more than 200 others to create a crisper, deeper understanding of customer purchasing patterns and the key drivers that can increase your LTV to CAC ratio. Want to see just how easy it is? Sign up for a free demo and we’ll walk you through it step-by-step!
If you’re already using CorralData, here’s how to use our AI-powered platform to calculate LTV to CAC:
Step 1: Complete your basic setup for LTV
Choose from our list of pre-built connectors to easily connect your e-commerce platform (Shopify, Magneto, BigCommerce, WooCommerce, etc.) to identify which purchases belong to which unique customer.
We highly recommend using consistent UTM tracking for all links to your website, when possible, to enable channel-specific LTV calculations.
Step 2: Complete your basic setup for CAC
Connect all your paid media platforms—our pre-built connectors make this simple, too—to get cost data from Google Ads, Meta Ads, Twitter Ads, and more into Corral.
Here as well, using consistent UTM tracking in all ad destination links will enable channel-specific CAC calculations. We also recommend setting up separate paid media campaigns to exclude existing customers and that are solely focused on new user acquisition to get a more accurate CAC calculation
Step 3: Build metrics for LTV & CAC
Once the needed data is imported into CorralData, there are multiple ways to calculate each metric.
- You can request these metrics to be built by our on-call human data team
- You can use natural language AI queries—this is our Ask AI tool— to build the metrics for you
- If you are somewhat familiar with SQL, you can build it yourself using our no-code SQL generator and import it onto a board
- If you are highly skilled in SQL, you can build it yourself
Further, and as mentioned above, you may be interested in calculating LTV and CAC on a per-channel basis if you have the needed UTM data flowing into your e-commerce platform. This would be helpful, for example, if you run ads to acquire new customers on both Google Ads and Meta Ads. We would recommend calculating the below for the most insightful and actionable reports:
- Google Ads CAC & LTV: Only looks at customers & orders that were acquired from Google Ads
- Meta Ads CAC & LTV: Only looks at customers & orders that were acquired from Meta Ads
- Paid Media CAC & LTV (Google Ads + Meta Ads): Only looks at customers & orders that were acquired from Paid Media by adding up LTV and CAC for both paid media channels
- Blended CAC & LTV (Use all acquired users, regardless of their source): Looks at all customers and orders and uses total paid media spend for CAC
To calculate each of the metrics above, simply divide the CAC by LTV.
In short:
- The LTV to CAC ratio provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of a company’s marketing efforts and its overall profitability.
- To calculate the LTV to CAC ratio, calculate LTV using your e-commerce platform and CAC by dividing marketing expenses by the number of newly acquired customers.
- Strive for a 3:1 ratio or higher for this metric!
- CorralData makes the process of calculating LTV to CAC radically simple by organizing and linking up customer data from multiple platforms.







































